The 5-Minute Rule for The Physical and Developmental Intersection: Examining Hypermobility in Individuals on the Autism Spectrum

Dropping Light on a Complex Connection: Evaluating Research on Hypermobility in Autistic Populations
Autism Sphere Problem (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental problem defined through troubles in social communication, interaction problem, and recurring behaviors. It influences people in a different way, along with a large assortment of symptoms and extent amounts. Over the years, analysts have been discovering the different aspects of ASD to better recognize its underlying causes and possible co-occurring health conditions. One such location of interest is the hookup between hypermobility and autism.
Hypermobility recommends to an extreme assortment of action in joints, enabling for more significant flexibility than normally noted in people without this condition. While hypermobility can easily be current separately as a curable attribute, it has additionally been found to exist side-by-side with particular medical conditions such as Ehlers-Danlos syndrome or Marfan syndrome. Lately, analysts have begun checking out the occurrence of hypermobility in autistic populations and its possible implications.
Several studies have reported a much higher incidence of shared hypermobility among people along with autism contrasted to the standard population. In one study conducted through Eccles et al. (2014), it was found that 67% of children identified with autism showed joint hypermobility to differing levels. Yet another research by Wingate et al. (2018) mentioned identical seekings, advising that shared hypermobility may definitely be more popular among people on the autism sphere.
The investigation discovering the web link between hypermobility and autism goes beyond simply establishing a relationship; it looks for to understand the possible devices underlying this organization. One theory put forth by researchers is that oddities in connective tissue may contribute to both hypermobility and autistic qualities. Combinative cells gives architectural support throughout the physical body, consisting of joints, ligaments, ligaments, and skin layer.
Combinative tissue disorders are recognized to influence bovine collagen manufacturing or structure – collagen being one of the primary parts of combinative tissue - and have been linked with both hypermobility and particular autistic characteristics. This recommends a prospective shared hereditary or natural process between hypermobility and autism. However, further investigation is required to totally clarify this relationship.
The implications of the hypermobility-autism hookup prolong beyond academic inquisitiveness. Understanding this hyperlink could possess practical implications for the prognosis and therapy of people on the autism spectrum. For occasion, joint hypermobility may influence electric motor capabilities advancement in children with ASD, likely influencing their potential to execute everyday activities or engage in physical tasks.
Additionally, realizing the existence of shared hypermobility in individuals with autism could aid medical care carriers in identifying co-occurring health conditions or comorbidities that might call for specific assistances or management methods. It could possibly also update therapeutic approaches customized to resolve the distinct requirements of people along with both ASD and hypermobility.
It is significant to take note that not all individuals along with autism are going to display joint hypermobility, nor are going to all people along with shared hypermobility possess autism. The relationship between these two conditions stays sophisticated and varied. Further study is essential to comprehend the underlying systems driving this association fully.
In verdict, exploring the link between hypermobility and autism gives beneficial ideas right into the intricate attribute of ASD and its prospective co-occurring health conditions. The investigation conducted thereby much suggests a higher incidence of shared hypermobility one of people on the autism spectrum reviewed to the basic population.
Understanding this association has actually efficient ramifications for medical diagnosis, procedure, and support solutions for those affected through both ailments. Through dropping illumination on this complex link, scientists are paving the way for improved understanding and care for autistic populaces who may also experience joint hypermobility.
Endorsements:
Eccles, J., Owens, G., Mathias, K., & MacDonald-Wallis, C. (2014). Shared Hypermobility Syndrome: A Common Clinical Disorder Associated With Autism Spectrum Problems? Autism Research Journal International Society for Autism Research, 7(5), 574–581. https://doi.org/10.1002/aur.1399
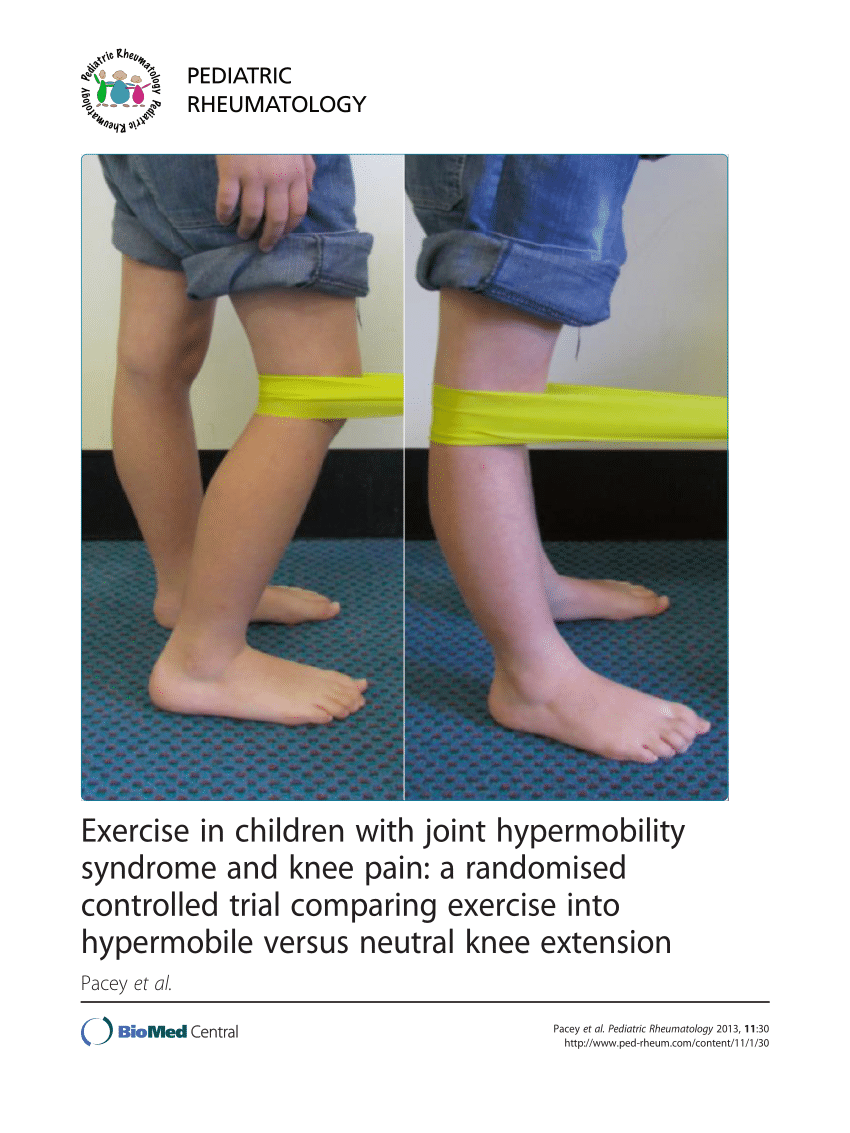
Wingate, M., Kirby, A., Petty, C., Ciciolla, L., Pinkham, L., & Briefer, P. (2018). Correlation between hypermobility and autism in Autism Spectrum Disorders: Underlying Symptomatology and Shared Etiology. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 48(3), 716–725. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-017-3361-3
